Caffeine AnhydrousDC
Caffeine is a bitter, white crystalline methylxanthine alkaloid and purine derivative, structurally related to adenine and guanine. It occurs naturally in various plant sources, notably coffee beans, and can be commercially synthesized from dimethylurea and cyanoacetic acid. Pharmacologically, caffeine is primarily known for its effects on mental alertness and is investigated for other applications including headache, migraine, and athletic performance.
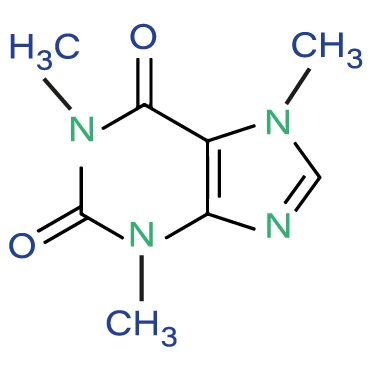
- Chemical Name - 1,3,7-Trimethyl-3,7-dihydro1H-purin-2,6-dione or 7-methyltheophylline
- Chemical Formula - C8H10N4O2
- CAS No. - 58-08-2
- Pharmacopoeia - IP / BP / USP / Ph.Eur
- Molecular Weight - 194.2 (anhydrous)
- Purity - 99.9%
| Description | Silky white crystalline, white glistening needles or a white Description Transmittance Absorbance Foreign Particles Typical Impurities Packaging End Use crystalline powder; odourless; sublimes readily. |
|---|---|
| Transmittance | NLT 60% |
| Absorbance | NMT 0.15% |
| Foreign Particles | NMT 50 ppm |
| Typical Impurities | Theophylline / isocaffeine / theobromine / 1,7-dimethyl-3,7 dihydro-1H-purine-2,6-dione |
| End Use | Stimulates the central nervous system, causing increased alertness. Caffeine gives most people a temporary energy boost and improves mood. Caffeine is in tea, coffee, chocolate, many soft drinks, and pain relievers and other over-the-counter medicines and supplements. |
| Treatment | Beverages, Neutraceuticals, Pharmaceuticals |
